Setting Up a New EC2 Linux Instance
I recently decided to purchase a reserved t3.nano instance to run some Docker containers and for general testing purposes. In addition to the default volume I decided to add a new one to separate my files from the OS. It required a few steps to get everything in place so I decided to post this mostly for future reference!
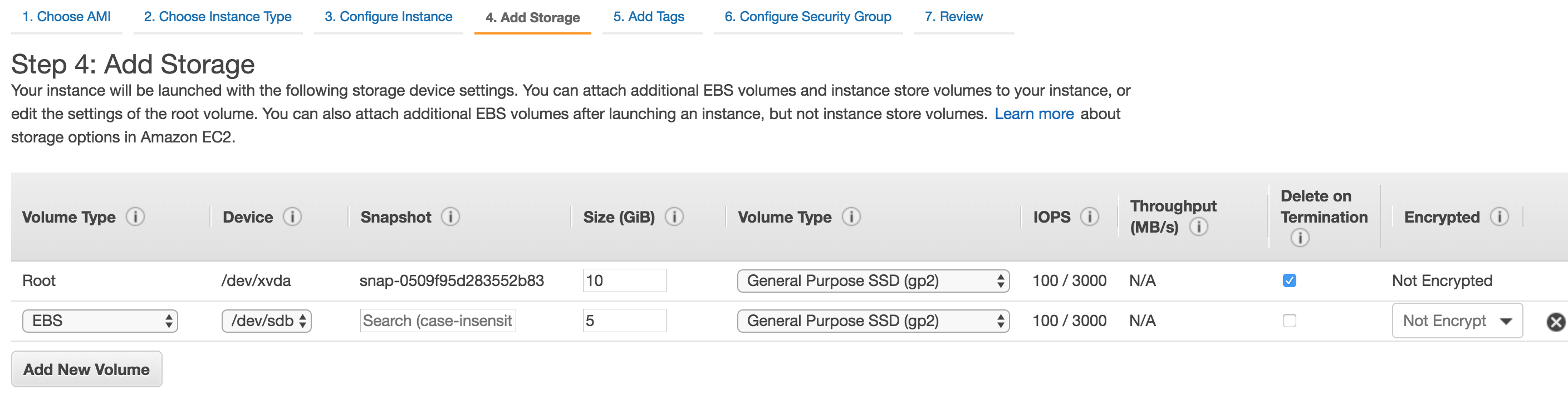
Attach a volume during creation
First I added a new volume to the instance while creating it.
Connecting to instance
Now we have to connect to the instance to format the new volume. To achieve that we must have access to the private we generated while we created the instance. So to SSH into the machine we run this command:
ssh -i {/Path/To/Key/file_name.pem} ec2-user@{public DNS name of the instance}
Format the volume
I found some AWS documentation to achieve this which was very useful: Making an Amazon EBS Volume Available for Use on Linux
No need to repeat every command in that documentation. It’s a simple step-by-step guide. Just follow it and you have a volume in use which is also mounted at start up.
Install and configure Docker
Installing Docker is as simple as running this:
sudo yum update -y
sudo yum install -y docker
To be able to use Docker without sudoing everything ad ec2-user to docker group:
sudo usermod -aG docker ec2-user
We need to make sure that Docker daemon starts on reboot too. To achieve this run this:
sudo systemctl enable docker
Copy files to the instance
To copy some files to the new instance I used SCP command:
sudo scp -i {/Path/To/Key/file_name.pem} -r {/Path/To/Local/Folder/} ec2-user@{public DNS name of the instance}:/Remote/Folder
The issue was ec2-user didn’t initially have access to write on the remote folder. In that case you can run the following command to have access:
setfacl -m u:ec2-user:rwx /Remote/Folder